Understanding Strokes: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Strokes, often called “brain attacks,” are serious medical emergencies that occur when the blood supply to a part of the brain is interrupted. This can cause damage to the brain and affect the functions it controls, such as movement, speech, and cognition. Early recognition and treatment are essential to improving outcomes.
What Is a Stroke?
A stroke happens when the brain doesn’t receive enough oxygen and nutrients due to a blocked or ruptured blood vessel. Without this supply, brain cells begin to die, leading to impairment in various body functions.
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
Also known as a “mini-stroke,” a transient ischemic attack (TIA) occurs when blood flow to the brain is temporarily interrupted. Symptoms typically resolve within a short time and cause no lasting damage. However, a TIA is a warning sign of a potential full stroke in the future.
Common TIA Symptoms:
- Numbness or weakness (especially on one side of the body).
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
- Vision problems.
- Dizziness or loss of balance.
- Severe headaches.
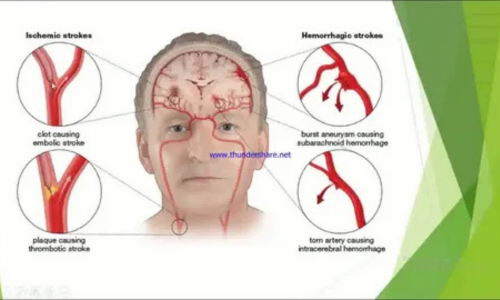
Types of Strokes
- Ischemic Stroke:
- Caused by a blockage in the blood vessels leading to the brain.
- Often linked to fatty deposits or blood clots.
- Hemorrhagic Stroke:
- Occurs when a blood vessel bursts, causing brain swelling and damage.
- Commonly caused by uncontrolled high blood pressure.
Risk Factors for Stroke
Several factors increase the likelihood of experiencing a stroke:
- Medical Conditions: High blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, cardiovascular disease.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, obesity, lack of exercise, and drug abuse.
- Other Factors: Advanced age, family history of heart disease, or previous transient ischemic attacks.
Recognizing Stroke Symptoms
Quick recognition of stroke symptoms can save lives. Use the BE FAST method:
- Balance: Sudden dizziness or loss of balance.
- Eyes: Blurred or double vision.
- Face: Drooping on one side of the face.
- Arms: Weakness or numbness in one arm.
- Speech: Difficulty speaking or slurred words.
- Time: Seek immediate medical help if you notice these symptoms.
Complications of a Stroke
Strokes can lead to serious complications, including:
- Paralysis or weakness on one side of the body.
- Difficulty speaking or understanding language.
- Memory loss or cognitive impairment.
- Depression and emotional changes.
- Blood clots in the legs or other infections.
Stroke Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diagnosis: CT scans, MRIs, and cardiovascular evaluations help identify the type and location of the stroke.
- Treatment:
- Medications such as blood thinners or clot-dissolving drugs to restore blood flow.
- Surgery to remove blood clots or repair damaged blood vessels.
- Rehabilitation therapies, including physical, occupational, and speech therapy.
Prevention Tips
Reducing your risk of stroke involves managing your health and adopting a healthy lifestyle:
- Monitor Health: Keep conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol under control.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular issues.
- Control Blood Pressure: Follow your doctor’s advice and take prescribed medications as directed.
Take Action
Being informed about strokes can save lives. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking prompt medical attention can significantly improve recovery and reduce long-term complications. Prioritize your health and adopt preventive measures to protect yourself from strokes.
Leave a Reply